Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) have become popular in the financial world, combining the flexibility of stock trading with the broad diversification of mutual funds. They’re appealing to a range of investors, from beginners to seasoned pros, offering a straightforward way to gain exposure to various asset classes, including stocks, bonds, commodities, and more. This blog will dive into what ETFs are, how they work, their benefits and risks, and tips for choosing the right ETF for your portfolio.
What is an ETF?
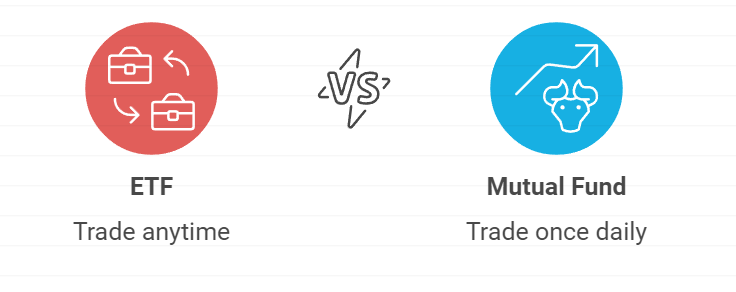
An ETF is a type of investment fund that holds a collection of assets, such as stocks, bonds, or commodities, which tracks the performance of a particular index or sector. Unlike mutual funds, which are only traded once daily, ETFs are traded on stock exchanges throughout the day, just like individual stocks.
For example, the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY) follows the S&P 500 index, providing investors with exposure to 500 large U.S. companies. By purchasing shares in SPY, an investor effectively gains exposure to the S&P 500’s performance without needing to buy each individual stock in the index.
How Do ETFs Work?
ETFs are designed to mimic the performance of an underlying index, sector, or asset class. Here’s a simple breakdown of the ETF process:
Creation: ETF providers create shares in an ETF by assembling the underlying assets in the fund. These providers work with authorized participants (often large financial institutions) to purchase or borrow the securities required for the ETF.
Management: ETFs are generally passively managed, meaning they aim to track a specific index rather than outperform it. This passive management often results in lower fees compared to actively managed funds, which is a major draw for many investors.
Trading: ETFs are listed on major stock exchanges and traded like stocks. Their prices fluctuate throughout the day based on supply and demand, unlike mutual funds, which are priced only once at the end of the trading day.
Dividends and Distributions: If an ETF holds income-generating assets, like dividend-paying stocks or bonds, it may pay out dividends to shareholders, usually on a quarterly basis.
Types of ETFs
ETFs come in various types, each with its unique characteristics and focus. Here are some of the most popular:
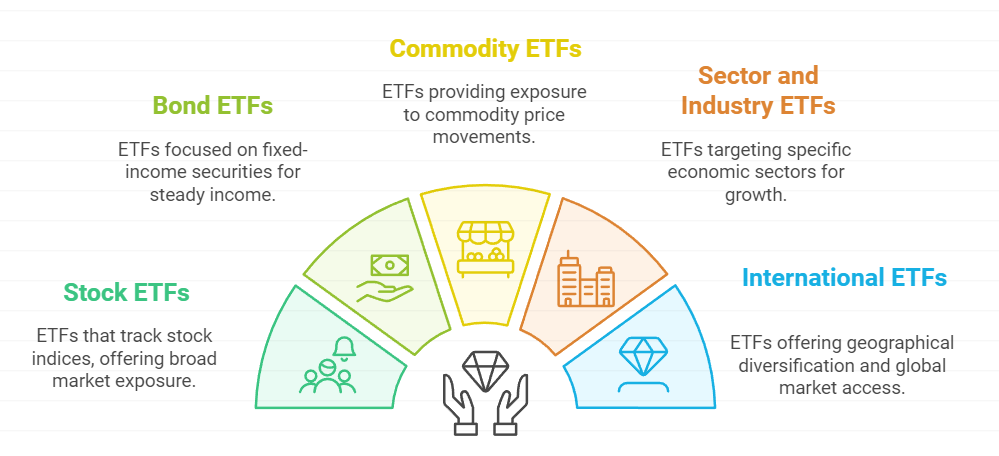
Stock ETFs: These ETFs hold a collection of stocks, often following a particular index like the S&P 500 or the Nasdaq 100. Stock ETFs allow investors to gain exposure to a broad range of companies without buying individual stocks.
Bond ETFs: These ETFs focus on fixed-income securities, including government, municipal, or corporate bonds. Bond ETFs can help investors gain steady income and diversify their portfolios.
Commodity ETFs: These ETFs give investors exposure to commodities like gold, silver, oil, or agricultural products. Rather than purchasing the commodity directly, you can invest in a commodity ETF to gain exposure to its price movements.
Sector and Industry ETFs: These ETFs focus on specific sectors like technology, healthcare, or energy. Investors use them to target certain parts of the economy and take advantage of sector growth trends.
International ETFs: These ETFs provide exposure to global markets, including emerging markets and foreign companies. They help investors diversify geographically and benefit from international growth.
Inverse and Leveraged ETFs: These are specialized ETFs that aim to deliver multiplied (or inverse) returns of a particular index. For example, a leveraged ETF might offer double the daily return of an index, while an inverse ETF gains when the index declines. They’re designed for short-term trading rather than long-term investment.
Advantages of ETF Investing
ETFs offer several benefits, which have contributed to their popularity among investors:
Diversification: By holding multiple assets in a single fund, ETFs offer broad market exposure. For example, a single share in a global stock ETF may give you access to hundreds of companies across various countries.
Liquidity and Flexibility: Since ETFs trade on exchanges like stocks, they offer high liquidity. You can buy or sell shares throughout the trading day, allowing for quick portfolio adjustments.
Low Costs: ETFs generally have lower expense ratios than mutual funds because they’re passively managed. These lower costs can have a significant impact on long-term investment returns.
Transparency: Most ETFs disclose their holdings daily, providing transparency for investors who want to know what assets they’re exposed to.
Tax Efficiency: ETFs can be more tax-efficient than mutual funds due to their unique structure. When shares are sold, they’re done so on the open market, often reducing taxable events.
Risks of ETF Investing

While ETFs have numerous benefits, they’re not without risks. Here are some to consider:
Market Risk: Like all investments, ETFs are exposed to market risks. If the assets within an ETF decline, the ETF’s value will drop as well.
Tracking Error: Sometimes, ETFs may not perfectly track their target index. This “tracking error” can be minimal for large, established ETFs but may be more pronounced in smaller or specialized funds.
Liquidity Risk: Some ETFs, especially those that focus on niche or international markets, may have lower trading volumes, resulting in wider bid-ask spreads and potential difficulties in quickly buying or selling shares.
Counterparty Risk in Synthetic ETFs: Some ETFs use derivatives like swaps to replicate their index. This introduces counterparty risk, as the ETF’s performance depends on the solvency of the swap issuer.
How to Choose an ETF
With thousands of ETFs available, selecting the right one for your investment goals can be challenging. Here are some factors to consider:
Investment Goals: Determine what you want to achieve. Are you looking for growth, income, or diversification? A growth-oriented investor might look for a technology ETF, while an income-focused investor might prefer a bond or dividend ETF.
Expense Ratio: The expense ratio is the annual fee that ETF providers charge investors. Lower expense ratios are usually better, especially for long-term investments.
Performance and Benchmarking: Review the ETF’s historical performance and how well it tracks its index. A good ETF should closely mirror the index with minimal tracking error.
Fund Size and Liquidity: Larger, more established ETFs generally have better liquidity, narrower bid-ask spreads, and lower trading costs. Smaller ETFs may struggle with liquidity, which can affect your ability to enter or exit positions efficiently.
Underlying Assets: Always check the ETF’s holdings. Some ETFs may concentrate heavily in a few stocks or sectors, while others offer broader exposure. Make sure the holdings align with your diversification goals.
Tax Considerations
ETFs are generally tax-efficient, but investors should still be aware of potential tax implications:
Capital Gains Tax: When you sell an ETF for a profit, you may be subject to capital gains tax. If you hold the ETF for over a year, you may qualify for long-term capital gains rates, which are usually lower than short-term rates.
Dividends: Some ETFs distribute dividends. Depending on your tax jurisdiction, these dividends may be taxed at ordinary income rates or qualify for a lower tax rate.
International Taxes: Investing in foreign ETFs may expose you to foreign taxes, depending on the tax treaty between your home country and the country where the ETF is domiciled.
Popular ETF Strategies
ETFs can be used in a variety of ways, from passive investing to more advanced trading strategies. Here are some popular approaches:
Buy-and-Hold Strategy: Many investors use ETFs as part of a buy-and-hold strategy, holding onto the funds for long-term growth. This approach is popular for retirement accounts.
Sector Rotation: Sector rotation involves moving investments between sectors based on economic cycles. For example, an investor might focus on technology during growth phases and utilities in downturns.
Thematic Investing: Thematic ETFs allow investors to focus on emerging trends like renewable energy, artificial intelligence, or e-commerce. These funds target specific industries that are poised for growth.
Income Generation: Investors seeking regular income might choose dividend-focused ETFs or bond ETFs, which distribute income to shareholders.
How QuantL AI Can Help You Succeed
At QuantL AI, we are committed to helping traders, from beginners to experienced investors, succeed in the Forex market. We offer a range of automated trading solutions that simplify the process, allowing you to focus on your financial goals.
Why Choose QuantL AI’s Automated Trading Solutions?
User-Friendly Platform: Our platform is designed with simplicity in mind, making it easy for both beginners and experienced traders to navigate.
Customizable Strategies: You can tailor our automated strategies to align with your specific risk tolerance and trading goals, whether you’re seeking short-term gains or long-term growth.
Real-Time Market Data: Stay informed with real-time data and insights to make well-informed trading decisions.
24/7 Support: Our customer support team is available around the clock to assist you with any questions or concerns.
Conclusion
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) provide a versatile, cost-effective way for investors to access a variety of asset classes, from stocks to bonds to commodities. With benefits like diversification, liquidity, and low fees, ETFs are a valuable addition to many portfolios.
However, investors should be mindful of each ETF’s structure, underlying assets, and tax implications to ensure they align with their financial goals. Like any investment, ETFs carry risks, and evaluating these can help you make informed decisions tailored to your objectives and market outlook. A well-chosen ETF can enhance a portfolio’s resilience and growth potential, making it a powerful tool for both novice and seasoned investors.
At QuantL AI, we understand how critical it is to protect your trading strategies and sensitive data. Our cutting-edge trading platform not only helps you develop profitable strategies but also ensures they are safe and secure from cyber threats. With our real-time data, secure infrastructure, and expert support, you can focus on trading with confidence.
Ready to secure your algorithmic trading journey? Reach out to us today.
For more information on how our automated trading strategies can benefit you, visit quantl.ai or get in touch with our team at [email protected]. We’re here to support you every step of the way!





